Bear Market: How Far Will Stocks Drop and Will It Possibly Lead to a Recession?
Author: Charles Ouko
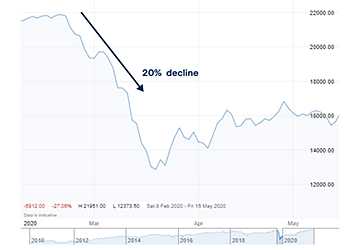
The S&P 500, an indicator of 500 top US publicly traded firms, touched its lowest point since March 2021 in June, causing a significant decline in the stock market's value.
The S&P 500 finished at 3,749 points on June 13 compared to a high of 4,818 points on January 4, a decline of 22%. The market values of well-known companies like Apple, Amazon, and Meta all suffered losses.
The decrease was the first time since the beginning of the COVID-19 epidemic that equities had entered the bear market territory, characterized by a protracted period of declining price patterns. (On the other hand, a bull market is one in which stock values continue to rise.)
Although there have been numerous bear markets previously, some analysts are concerned about a recession due to the current situation's rising inflation and other issues.
Here's everything you should know about bear markets: why they develop, how long this may continue, and what it implies for the economy.
A bear market.
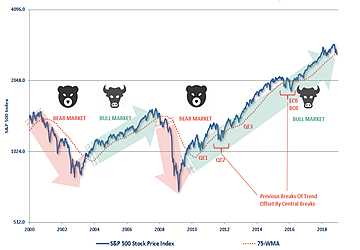
A bear market is characterized by a two-month continuous loss of at least 20% from recent highs in a major stock market index.
Hartford Funds estimates that the S&P 500 has experienced 26 bear markets since 1928.
Stockbroker confronts a bear's shadow.
A bear market has emerged for the first time in two years as the S&P 500 Index has continued to trade over 20% below its high in January 2022.
A bull market, the opposite of a bear market, occurs when a broad market index, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average or S&P 500, rises by 20% or more over a minimum of two months.
Additionally, according to Hartford Funds, there have been 27 bull markets from 1928, each lasting an average of 2.7 years or 991 days.
The average bear market, how long does it last?
Depending on your chosen formula, A bear market in the S&P 500 has typically lasted 289 days, or roughly nine and a half months, since the 20s. (The shortest was barely one month long and occurred in March 2020 during the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in the US.) The S&P 500 fell by nearly 36 percent on average throughout those downturns.
But recently, Bespoke Investment Group reports that the length of the 14 bear markets that have occurred since World War II has averaged 359 days or about a year.
Accordingly, the present bear market would end at the start of 2023, one year after its top in January.
Is a bear market a sign that a recession is approaching?
A recession and a bear market don't necessarily go hand in hand. According to Reuters, nine of the 12 recessions that occurred since bear markets followed World War II.
But since 1928, there have only been 15 recessions and 26 bear markets.
Bespoke Investment Group claims that bear markets associated with recessions are typically longer (495 days as opposed to 198 days) and severe (a decrease in the S&P 500 of 35% as opposed to 28.2%).







